Think You Know Science? Try This Challenging Quiz
If you enjoy pushing the limits of your knowledge, a challenging science quiz is the perfect way to test your understanding of the world around you. Science is enormous — from microscopic organisms to galaxies, from chemical bonds to cell biology, from the speed of light to the mysteries of the universe. This quiz brings together some of the most interesting and mind-expanding scientific concepts.
Each question comes with a detailed explanation to help you learn deeply, not just memorize answers.
Hydrogen: The Most Abundant Element in the Universe
Hydrogen makes up more than 74% of all visible matter in the universe. It is the simplest atom, containing just one proton and one electron.
Hydrogen powers:
- Stars (through nuclear fusion)
- Nebulae
- The formation of galaxies
- The chemistry of life
Our Sun itself is mostly hydrogen, constantly fusing atoms into helium and releasing energy.
Albert Einstein and the Theory of Relativity
Einstein’s theory of relativity transformed modern physics. His ideas explained how space and time are interconnected, how gravity works, and how energy and mass are equivalent.
Key insights:
- Special relativity: the speed of light is the universal speed limit
- General relativity: gravity is caused by the curvature of spacetime
- E = mc² shows mass and energy are connected
Einstein’s theories underpin GPS, nuclear energy, astrophysics, and our understanding of black holes.

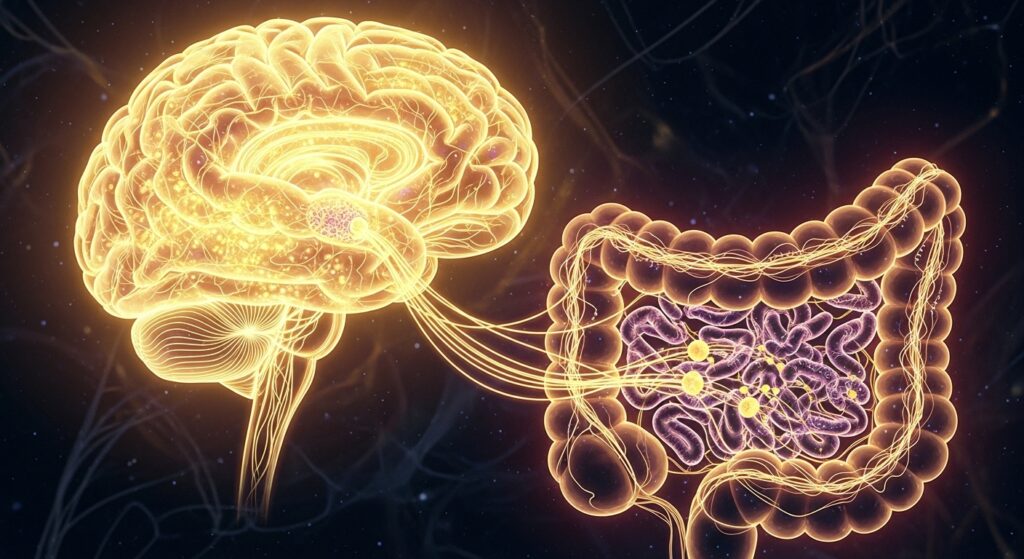
The Gut: The Body’s Second Brain
The human gut contains over 500 million neurons, making it the second-most neuron-rich organ after the brain. This enteric nervous system regulates digestion and communicates with the brain through the vagus nerve.
Reasons it’s called the “second brain”:
- It controls digestion independently
- Influences mood and emotions
- Produces neurotransmitters like serotonin
- Houses trillions of beneficial bacteria
Gut health is central to overall wellbeing.
Tardigrades: The Toughest Creatures on Earth
Tardigrades (water bears) can survive:
- Extreme radiation
- Boiling water
- Freezing temperatures
- The vacuum of space
- 1,000 times more pressure than the deep ocean
They enter a state called cryptobiosis, shutting down all metabolic processes until conditions improve.
These tiny creatures show scientists what life might look like on other planets.

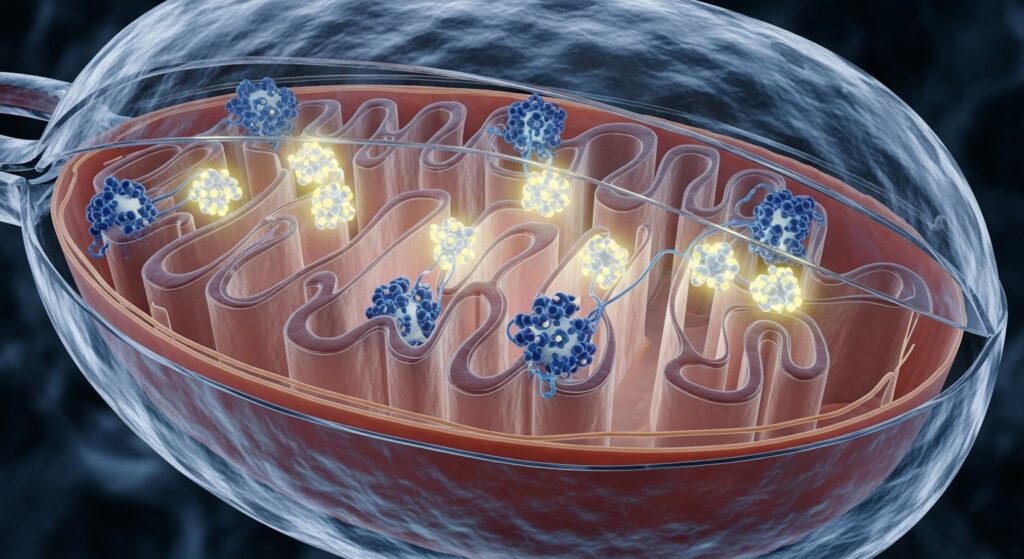
Mitochondria: The Powerhouse of the Cell
Mitochondria generate ATP, the energy currency of the cell, through cellular respiration. Almost every eukaryotic cell contains these remarkable organelles.
Mitochondria are unique because:
- They have their own DNA
- They originated from ancient bacteria (endosymbiosis theory)
- They regulate energy, metabolism, and cell death
Studying mitochondria helps us understand aging and metabolic diseases.
Covalent Bonds: Shared Electrons Build Life
A covalent bond forms when atoms share electrons. This is the most common bond in biological molecules.
Examples:
- Water (H₂O)
- DNA
- Proteins
- Sugars
- Cell membranes
Covalent bonds are responsible for the structure and stability of nearly all living systems.
Jupiter: The Planet With the Strongest Gravity
Jupiter has 2.5 times the mass of all other planets combined. Its gravity is so strong that it influences comets, asteroid belts, and the orbits of other objects in the solar system.
Its gravity:
- Protects Earth by capturing asteroids
- Shapes surrounding space
- Compresses its core into metallic hydrogen
Jupiter acts like a cosmic shield for the inner planets.

South America: The Biodiversity Capital of Earth
South America — especially the Amazon rainforest — has the highest biodiversity on the planet. It is home to:
- 3 million+ insect species
- 40,000+ plant species
- 1,300+ bird species
- 430+ mammals
- Countless undiscovered species
The Amazon is responsible for regulating climate, carbon absorption, and rainfall globally.

Photosynthesis: Powering Life Through Sunlight
Photosynthesis uses sunlight to turn water and carbon dioxide into glucose and oxygen. It occurs in chloroplasts and is the foundation of the food chain.
Reasons it matters:
- Produces nearly all oxygen
- Feeds nearly all ecosystems
- Regulates atmospheric CO₂
- Supports life on Earth
Without photosynthesis, Earth would be lifeless.
The Speed of Light
Light travels at 299,792 km per second. This universal constant shapes physics, astronomy, and technology.
At this speed:
- Light reaches the Moon in 1.3 seconds
- The Sun’s light reaches Earth in 8 minutes
- A beam circles Earth 7.5 times per second
Nothing in the universe can surpass this speed.
Did This Challenging Science Quiz Push You?
This challenging science quiz explored physics, biology, chemistry, and astronomy, giving you a deeper and clearer understanding of the universe. By learning the explanations behind each answer, you strengthen your scientific knowledge and develop a sharper, more curious mind.
Quizzes like this are perfect for building long-term understanding and boosting your intellectual skills.