Animals and Nature Science Quiz: Test Your Knowledge About the Natural World
Nature is full of endless surprises, from tiny insects building complex societies to gigantic whales swimming across oceans. The natural world is a carefully balanced web of life, where every organism — plant, animal, fungus, or microbe — plays a role in maintaining ecological harmony. This animals and nature science quiz is designed to help learners explore fascinating facts about wildlife, ecosystems, and biological processes.

Nature invites curiosity, and every question in this quiz opens a small window into the extraordinary lifeforms that share our planet.
The Largest Mammal: A Giant Beneath the Waves
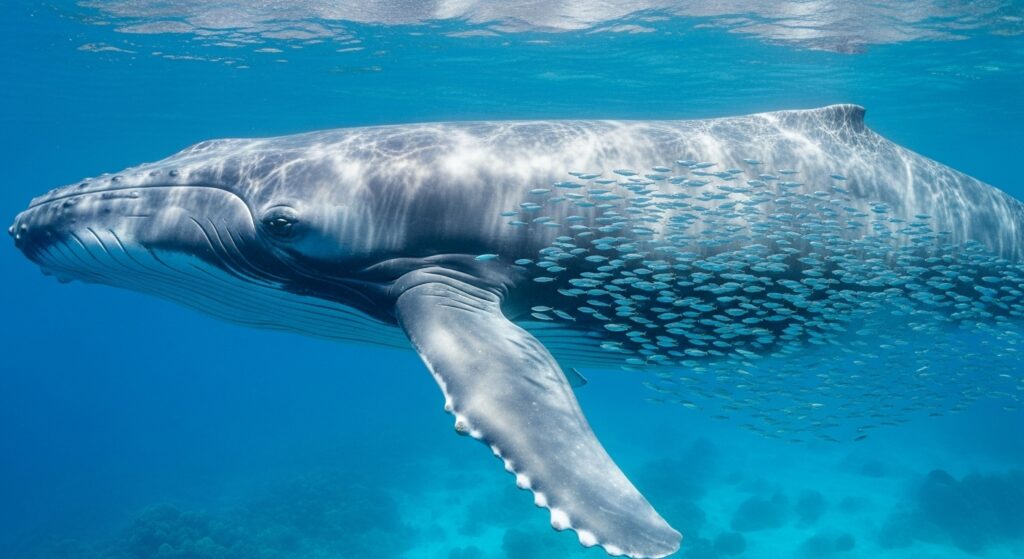
One of the quiz questions asks about the largest mammal on Earth, and the correct answer is the blue whale. Blue whales can grow up to 30 meters and weigh more than 180 tons, making them larger than any dinosaur that ever lived. These gentle giants feed mainly on krill — tiny shrimp-like animals — despite their enormous size. The ocean’s ability to support such massive creatures shows how ecosystems adapt to scale, offering the right food resources at the right time.
For more on blue whales, see:
https://www.nationalgeographic.com/animals/mammals/facts/blue-whale

Photosynthesis: Nature’s Energy Factory
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria convert sunlight into chemical energy. Using chlorophyll, these organisms transform carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen. This process is fundamental because it forms the base of almost every food chain. Without photosynthesis, there would be no breathable oxygen and almost no life.
A detailed explanation of the process can be found at:
https://www.britannica.com/science/photosynthesis
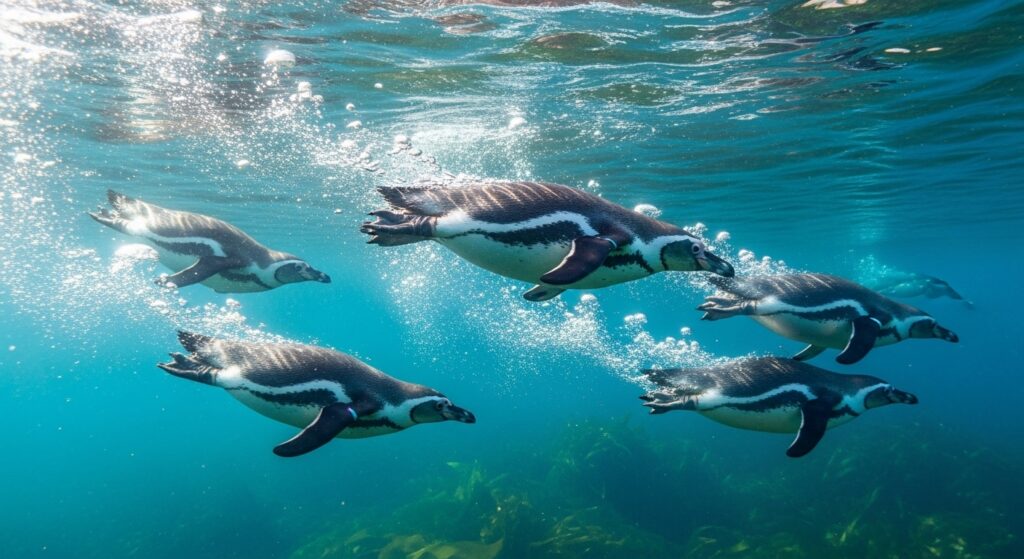
Birds That Don’t Fly: The Adaptations of Penguins
Penguins are often mistaken as clumsy walkers, but in water, they become extraordinary swimmers. These flightless birds have evolved powerful flippers, streamlined bodies, and dense bones that help them dive deep and maneuver quickly underwater. Their inability to fly is compensated by impressive aquatic agility. Penguins survive in extreme conditions using thick layers of fat and social behaviors like huddling for warmth.

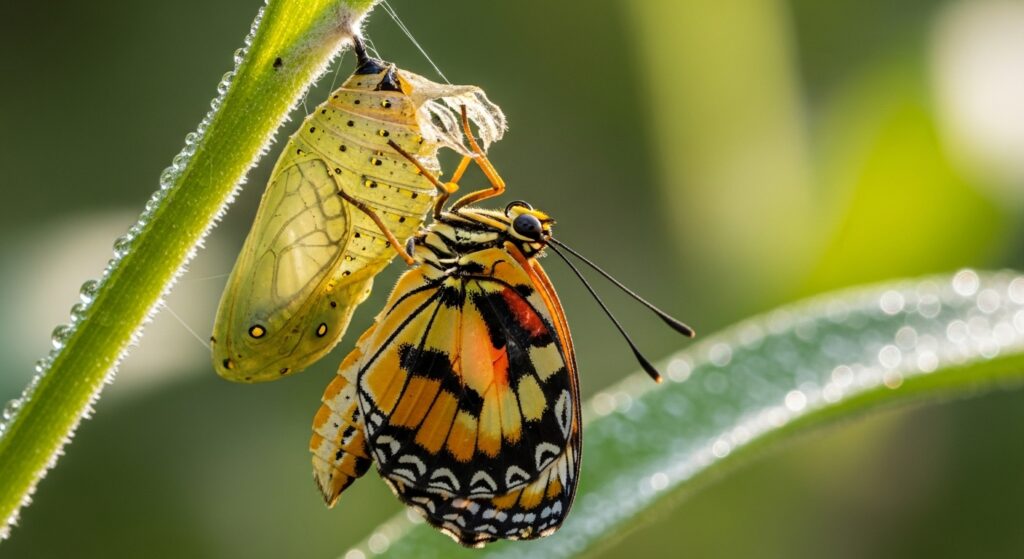
Metamorphosis: Transformations in the Insect World
The butterfly’s life cycle is one of the most famous natural transformations. Complete metamorphosis involves four stages: egg, larva (caterpillar), pupa (chrysalis), and adult. During the pupa stage, the organism undergoes a remarkable internal reorganization, reshaping tissues and forming wings. This dramatic change illustrates how insects adapt to different environmental niches throughout their lives.

Earth’s Atmosphere: A Protective Shield
Nitrogen makes up about 78% of Earth’s atmosphere. Many people assume oxygen is the most abundant gas, but nitrogen dominates because it is relatively inert. The atmosphere plays several vital roles: protecting Earth from harmful solar radiation, maintaining temperature, and allowing weather patterns to form. It also enables plants and animals to breathe and survive.
Learn more about atmospheric composition here:
https://www.noaa.gov/jetstream/atmosphere/gases

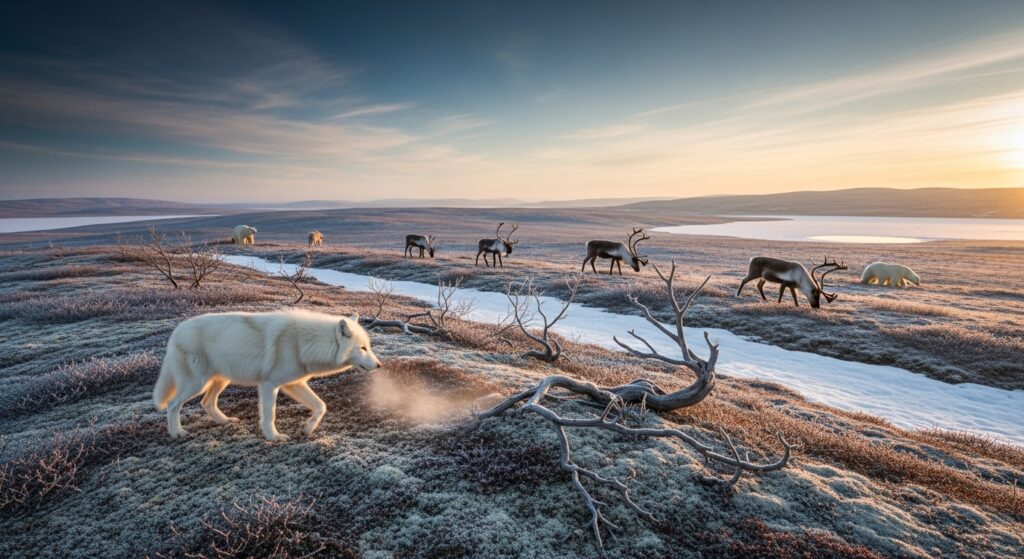
The Tundra: Life in Frozen Landscapes
The tundra biome is one of the harshest environments on the planet. It is characterized by freezing temperatures, strong winds, and permafrost — permanently frozen soil. Despite the extreme cold, the tundra hosts animals such as arctic foxes, snowy owls, caribou, and musk oxen. Plants in this biome grow close to the ground to avoid freezing and conserve warmth.

The Secret Work of Bees
Bees play a central role in pollination, helping flowers produce fruits and seeds. To make honey, bees gather nectar — a sugary liquid — and bring it back to their hive. Inside the hive, they convert nectar into honey using enzymes and evaporation. Honeybees also communicate using the “waggle dance,” which tells other bees where to find nectar-rich flowers.
More about bees’ behavior:
https://www.britannica.com/animal/honeybee
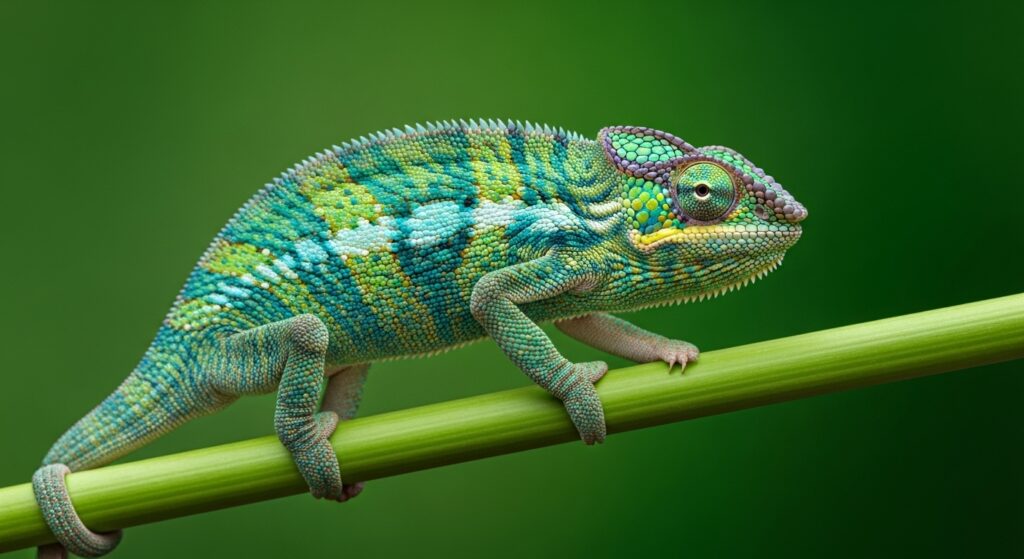
Camouflage Masters: The Chameleon
Chameleons are famous for changing their skin color, not just for camouflage but also for communication, temperature control, and mood expression. Their skin contains special pigment cells called chromatophores which expand or contract to alter the visible color. Chameleons also have independently moving eyes and long sticky tongues for catching insects.

Earth’s Tallest Trees: The Giants of the Forest
Coast redwood trees (Sequoia sempervirens) are the tallest trees in the world, reaching heights over 110 meters. They thrive in moist coastal environments where fog helps hydrate their needles. These ancient trees can live for more than 2,000 years and create complex forest ecosystems that support diverse wildlife.
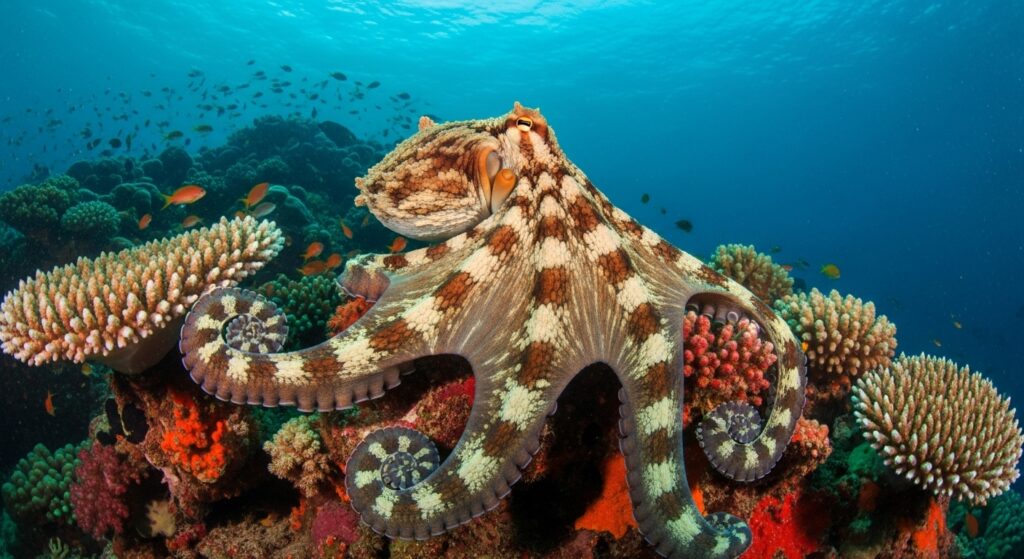
Ocean Wonders: The Octopus
Octopuses are among the most intelligent animals in the ocean. With eight arms lined with suction cups, they can manipulate objects, escape predators, and solve puzzles. Their ability to change color and texture allows them to blend into coral reefs, rocks, and sandy ocean floors. Their soft bodies let them squeeze through extremely narrow spaces, making them true escape artists.

Conclusion
The natural world is rich with extraordinary creatures and ecosystems, each adapted to survive in its own special way. From towering redwoods to shape-shifting chameleons, every organism contributes to Earth’s biodiversity. This animals and nature science quiz offers a glimpse into the complexity and beauty of nature, encouraging curiosity and deeper learning. Understanding animals and ecosystems helps us appreciate the balance of life — and reminds us why protecting our planet is so important.