Food and Nutrition Science Quiz: Test Your Knowledge About Healthy Eating
Food and nutrition play a central role in human health, energy, growth, and disease prevention. Every bite we eat contains nutrients that fuel our cells, repair tissues, support brain function, and maintain essential bodily processes.
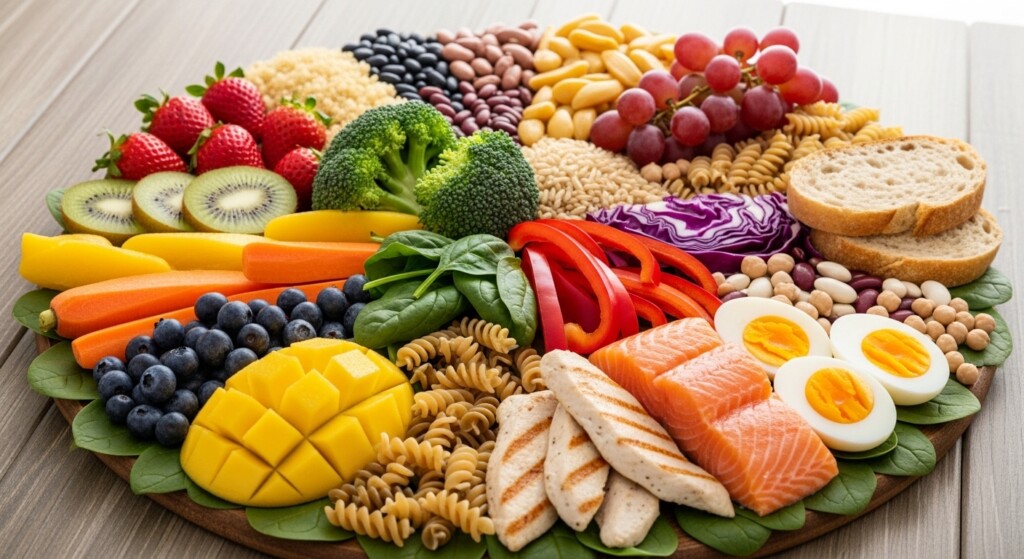

This food and nutrition science quiz helps learners test their knowledge of vitamins, minerals, macronutrients, and the science behind healthy eating habits. Nutrition is not just about what we eat—it is about how the body uses food to function, heal, and thrive.
Carbohydrates: The Body’s Main Energy Source
Carbohydrates are one of the three main macronutrients and provide the quickest energy for the body. When we eat foods like bread, rice, potatoes, and grains, they break down into glucose, which powers muscles and brain activity. Complex carbohydrates, such as whole grains, digest slowly and provide long-lasting energy, while simple sugars are absorbed quickly. Athletes rely heavily on carbohydrates for high-intensity activities.
Learn more about carbohydrate function here:
https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/carbohydrates

Vitamin D and Sunlight: A Natural Health Booster
Unlike most vitamins, Vitamin D can be produced when sunlight hits the skin. It plays a critical role in immune function, calcium absorption, and bone health. Many people are deficient due to indoor lifestyles, sunscreen use, or living in low-sunlight regions. Foods like fortified milk, egg yolks, and salmon also provide Vitamin D, but sunlight remains the richest natural source.
Calcium: The Foundation of Strong Bones and Teeth
Calcium is the most abundant mineral in the human body. It supports bones, teeth, muscle contractions, nerve signaling, and blood clotting. Children and teenagers especially need calcium for bone development, while adults require it to prevent osteoporosis. Dairy products, leafy greens, almonds, and fortified cereals are excellent sources.
More information on calcium:
https://www.britannica.com/science/calcium

Protein: Essential for Growth and Repair
Protein is a vital macronutrient made up of amino acids. It repairs tissues, builds muscles, strengthens the immune system, and produces enzymes and hormones. Animal sources like eggs, meat, and dairy are complete proteins, containing all essential amino acids. Plant-based proteins from beans, lentils, and nuts also contribute significantly to daily needs and support vegetarian diets.
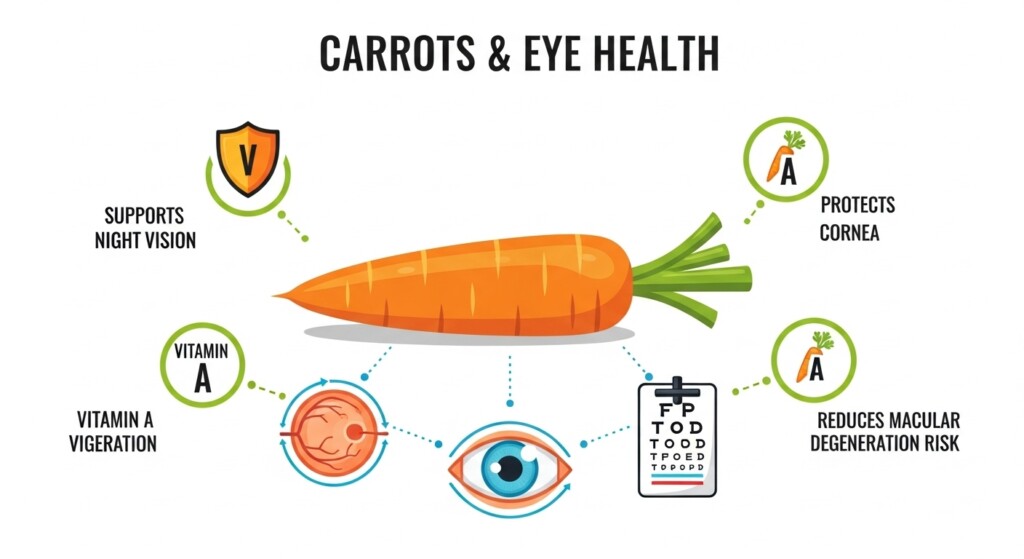
Vitamin A: Protecting Eyesight and Growth
Vitamin A supports vision, immune function, and skin health. Without Vitamin A, the eyes cannot adjust properly to darkness, leading to night blindness. Foods rich in Vitamin A include carrots, sweet potatoes, spinach, and liver. The body converts beta-carotene from orange vegetables into usable Vitamin A.
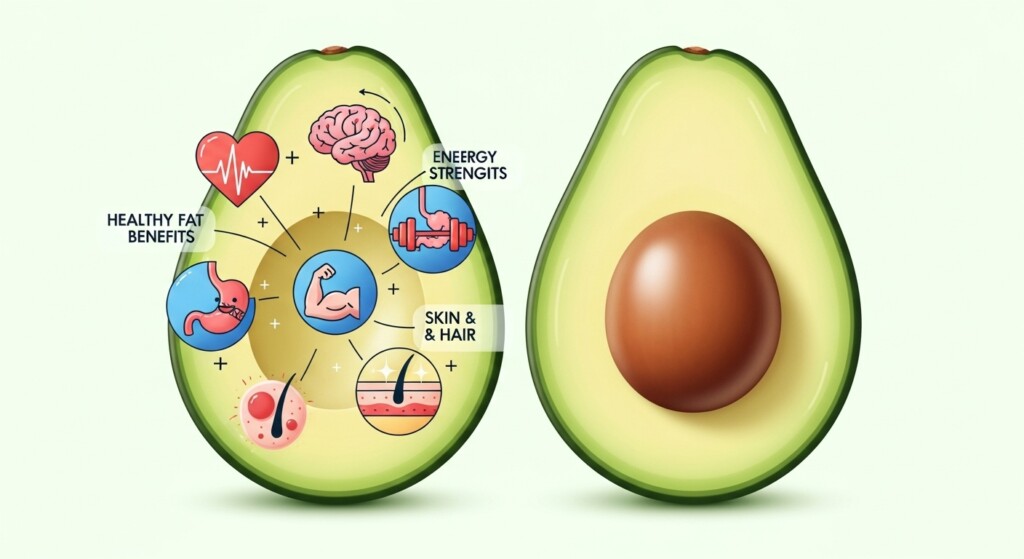
Healthy Fats: Understanding Unsaturated Fats
Not all fats are harmful. Unsaturated fats—found in foods like olive oil, avocados, nuts, and salmon—support brain function, reduce inflammation, and help absorb fat-soluble vitamins. In contrast, trans fats and excessive saturated fats increase the risk of heart disease. Learning to differentiate healthy fats from unhealthy ones is crucial for long-term wellness.
More about fats:
https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/fats
Fiber: Nature’s Digestive Helper
Dietary fiber is essential for digestion, gut health, and preventing constipation. It helps regulate blood sugar, supports weight control, and reduces the risk of heart disease. Fiber-rich foods include beans, whole grains, fruits, and vegetables. Insoluble fiber adds bulk to stool, while soluble fiber slows digestion and enhances nutrient absorption.

Potassium: Maintaining Fluid and Nerve Balance
Potassium is an electrolyte that helps regulate fluid balance, muscle contractions, and nerve signals. It works alongside sodium to maintain hydration and cellular function. Bananas, potatoes, oranges, and leafy greens are excellent sources. Too little potassium can cause muscle weakness and fatigue, while too much can be dangerous for people with kidney issues.
More on potassium’s role:
https://www.britannica.com/science/potassium
Vitamin C: Strengthening Immunity
Vitamin C is widely known for boosting the immune system. It helps the body fight infections, repair tissues, absorb iron, and neutralize harmful free radicals. Citrus fruits, strawberries, bell peppers, and broccoli are among the best sources. Vitamin C is water-soluble, meaning the body does not store it—regular intake is necessary for health.

Conclusion
Understanding nutrition empowers people to make healthier choices, prevent disease, and maintain long-term wellness. From the energy provided by carbohydrates to the immune-supporting power of Vitamin C, each nutrient plays a unique role in keeping the body functioning. This food and nutrition science quiz highlights the importance of balanced eating, nutrient-rich foods, and scientific knowledge about what we consume. Good nutrition is the foundation of a strong body, sharp mind, and healthy life.